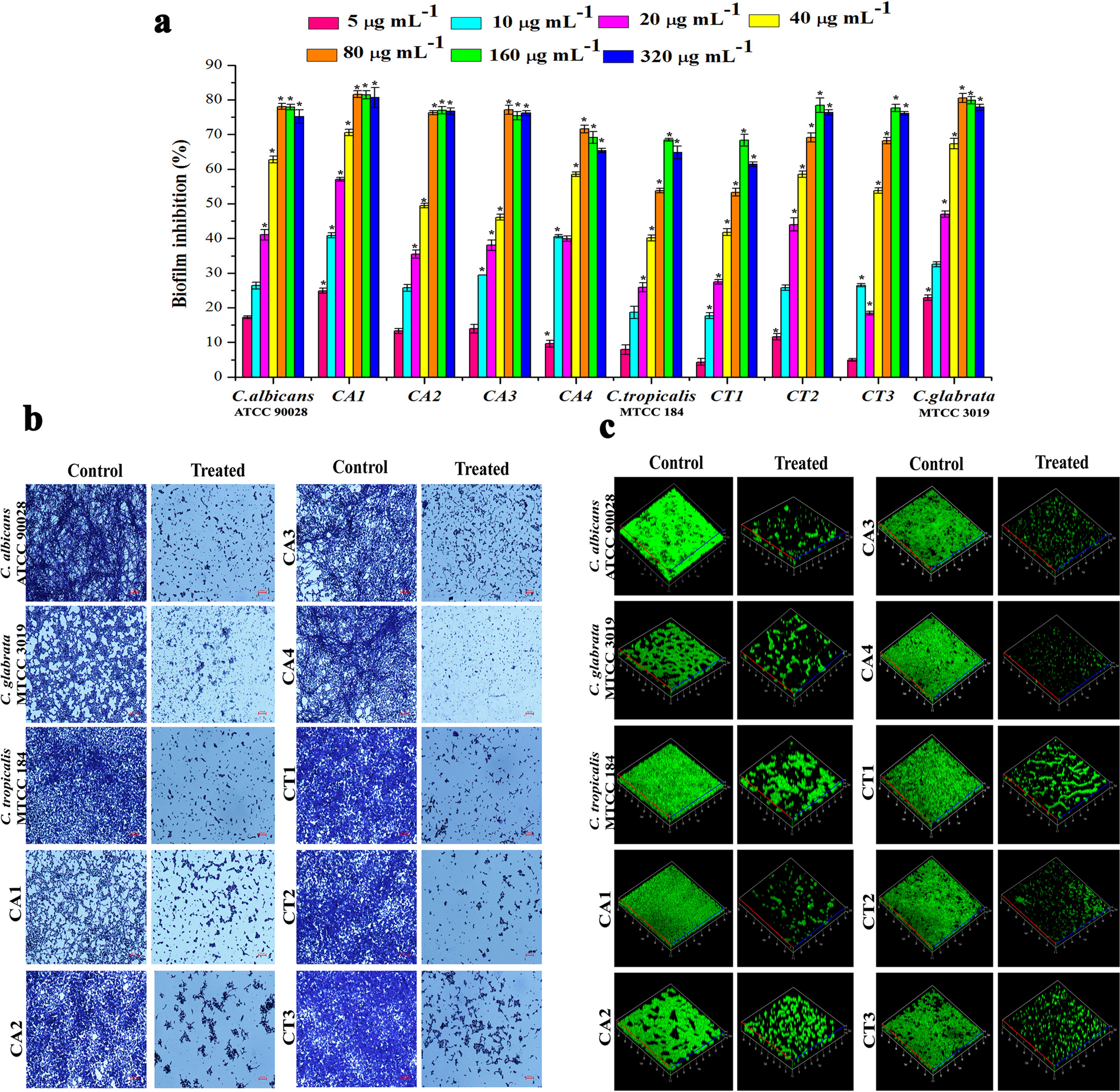
Global proteomic analysis deciphers the mechanism of action of plant derived oleic acid against Candida albicans virulence and biofilm formation | Scientific Reports

Global Secretome Characterization of the Pathogenic Yeast Candida glabrata | Journal of Proteome Research

Candida albicans Morphogenesis Programs Control the Balance between Gut Commensalism and Invasive Infection - ScienceDirect
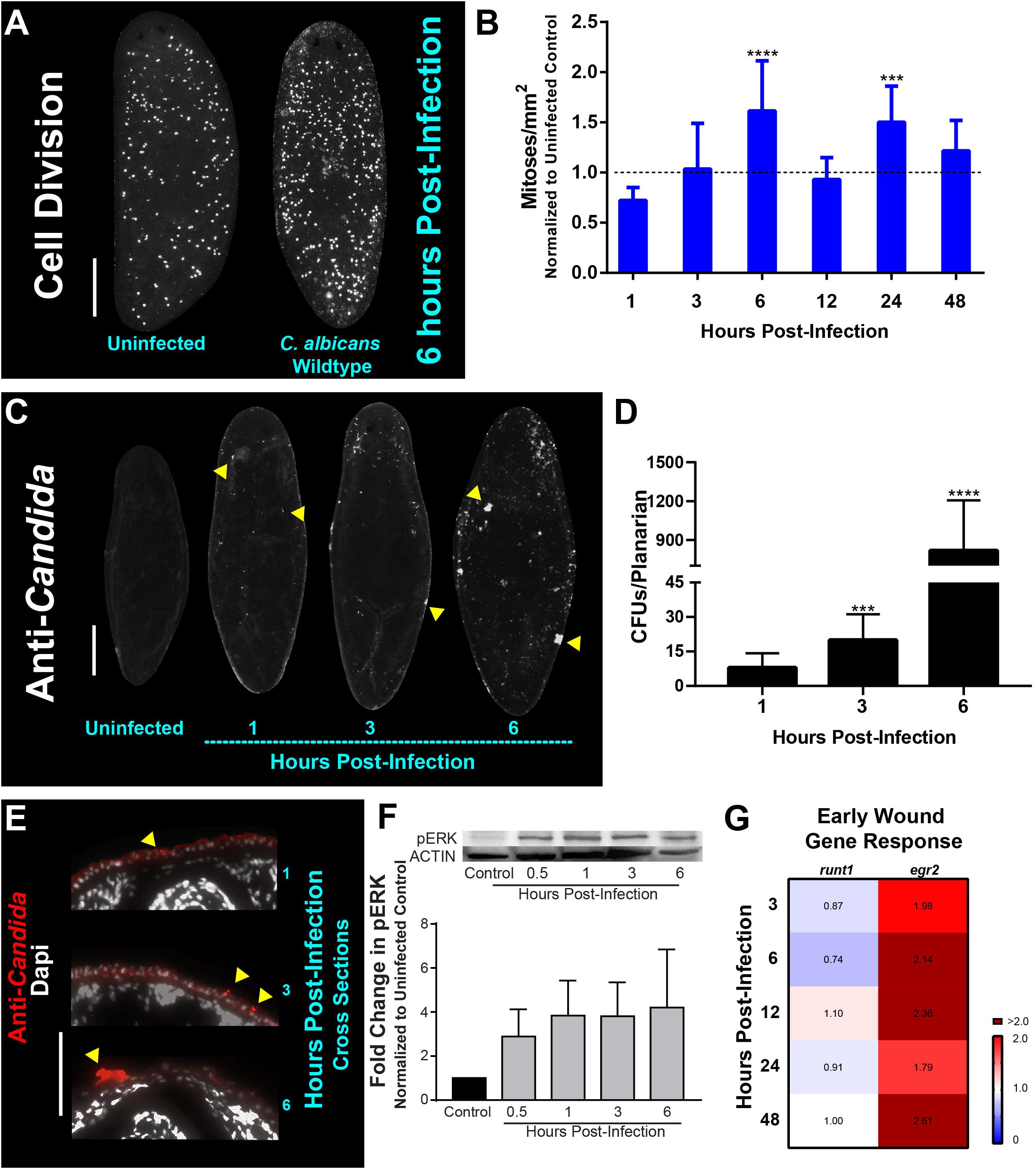
Frontiers | Epithelial Infection With Candida albicans Elicits a Multi-System Response in Planarians
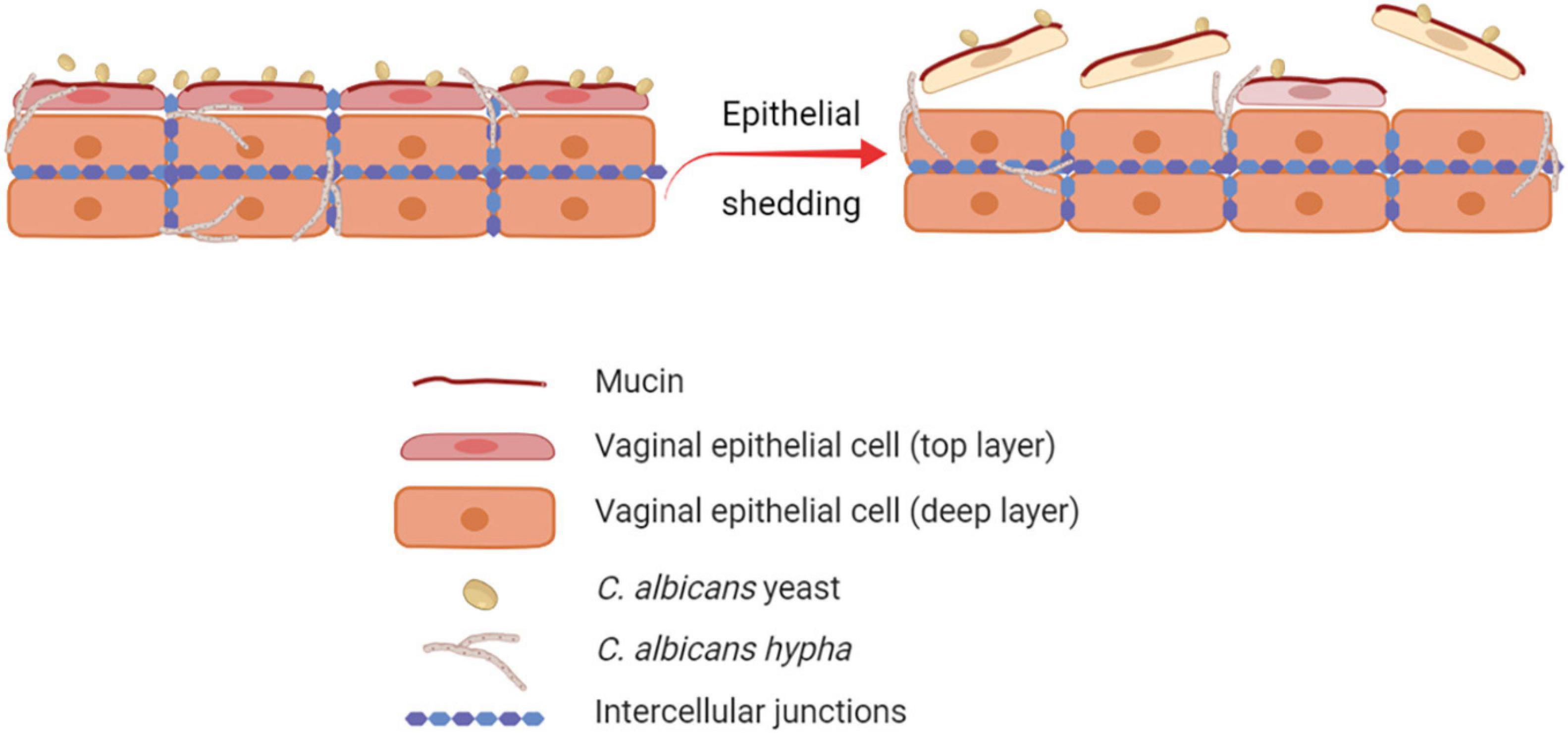
Frontiers | It Takes Two to Tango: How a Dysregulation of the Innate Immunity, Coupled With Candida Virulence, Triggers VVC Onset

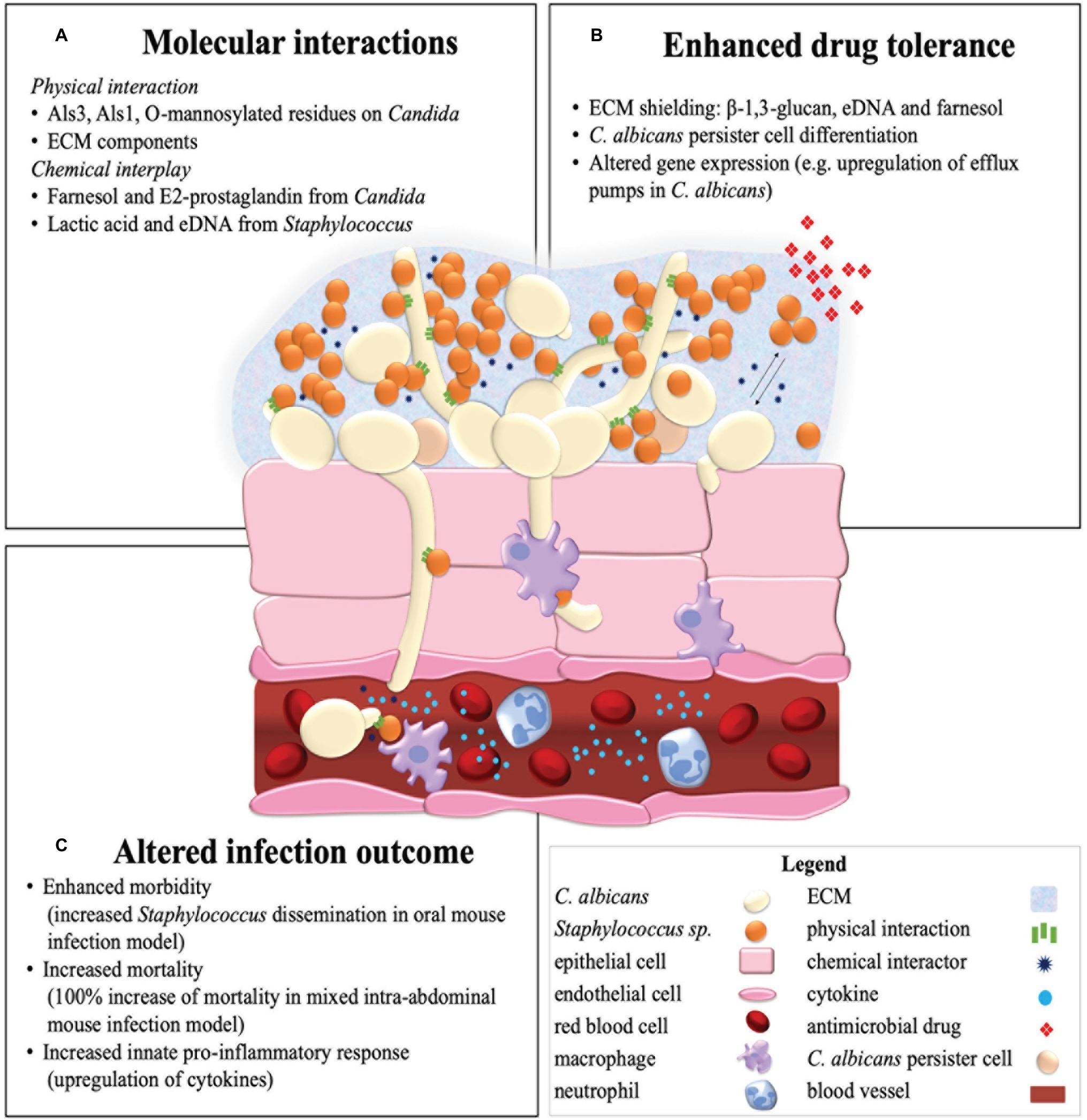
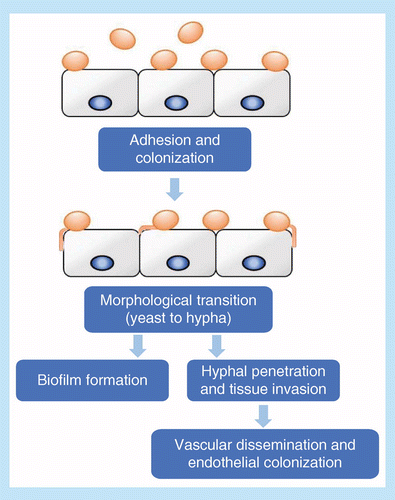
Metabolism impacts upon Candida immunogenicity and pathogenicity at multiple levels: Trends in Microbiology

The Candida albicans toxin candidalysin mediates distinct epithelial inflammatory responses through p38 and EGFR-ERK pathways | Science Signaling

The correlation of virulence, pathogenicity, and itraconazole resistance with SAP activity in Candida albicans strains

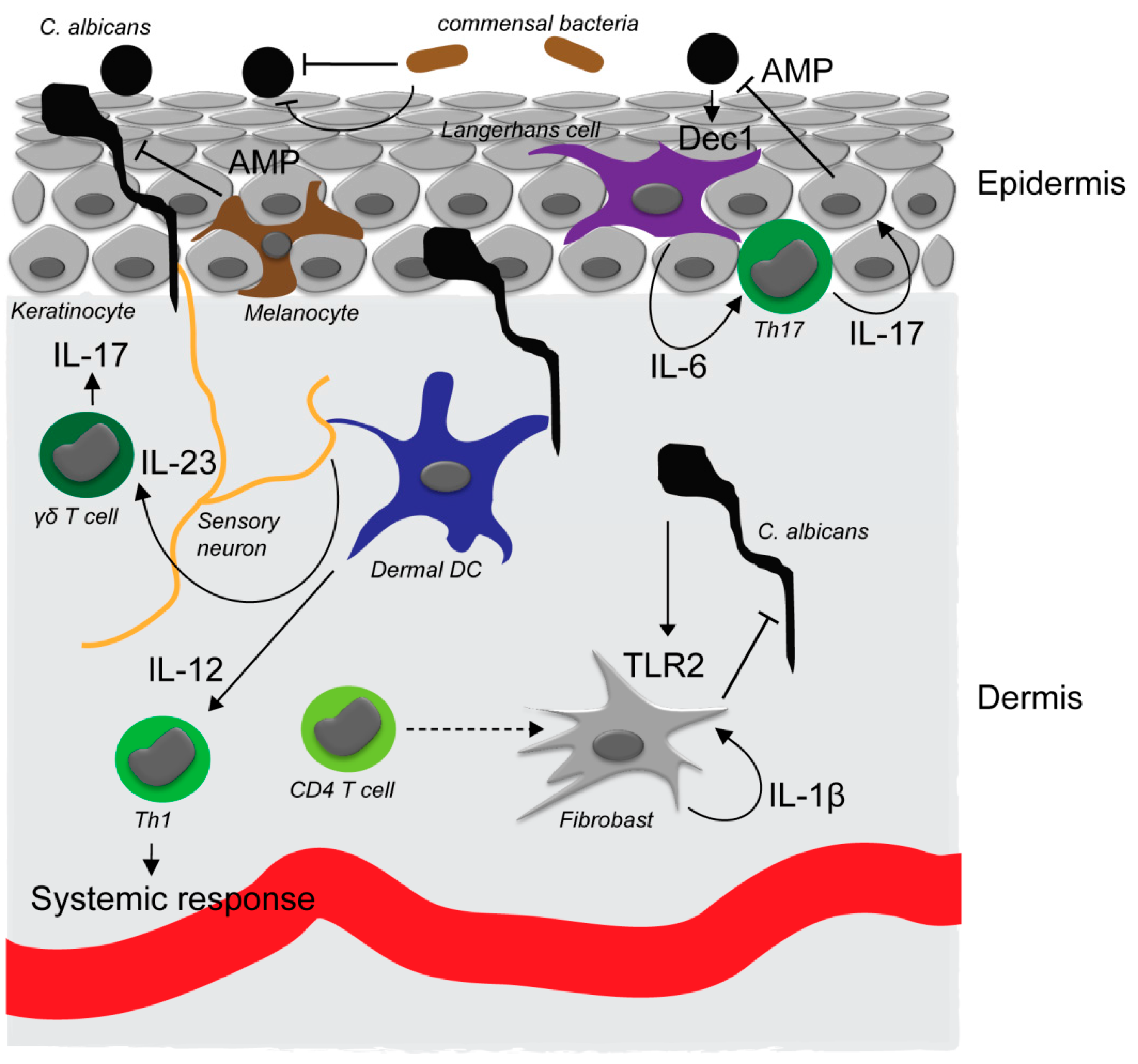
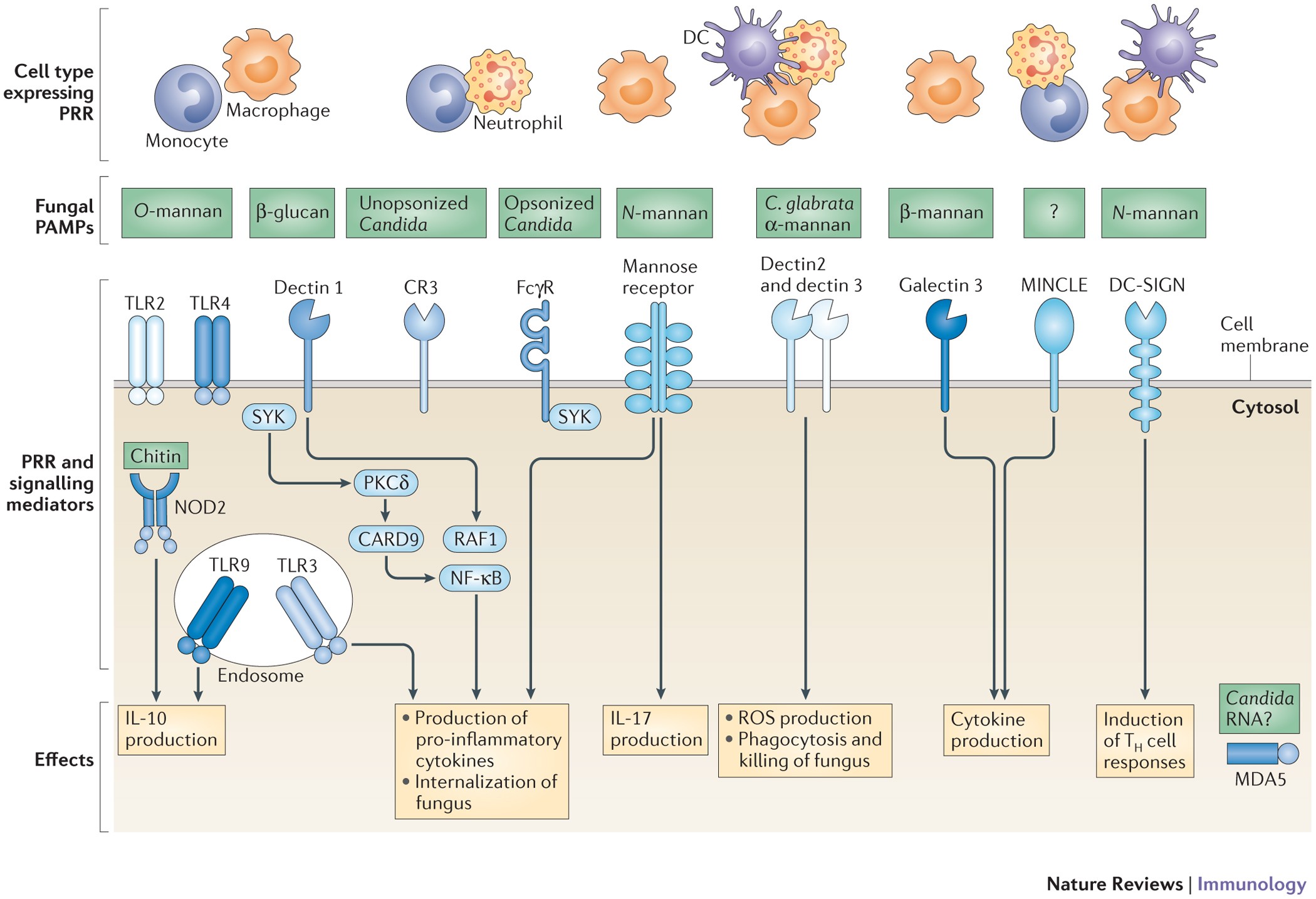
Frontiers | New Insights in Candida albicans Innate Immunity at the Mucosa: Toxins, Epithelium, Metabolism, and Beyond

Candida albicans Sap6 amyloid regions function in cellular aggregation and zinc binding, and contribute to zinc acquisition | Scientific Reports